Within the maxillary sinus which lies beneath the cheek bone on each side are mucous glands.
Mucus retention cyst floor maxillary sinus.
Maxillary sinus retention cysts are most often the result of inflammatory changes in the mucous membranes.
The lesion can fluctuate in size depending on its fluid filled state.
The aim of this study was to investigate the long term natural course of retention cysts of the maxillary sinus.
Types of mucous retention cyst the types of mucous retention cysts are divided into the regions they are found.
A maxillary sinus cyst is an abnormal tissue growth located in either of the cavities located behind the cheekbones on either side of the nose.
Cyst in the maxillary sinus is a common benign disease.
The lesion is a result of the extravasation of saliva from an injured minor salivary gland.
As there is no normal tissues regeneration and the excretory ducts patency of the mucous glands is not restored.
Symptoms are usually non existent but in some cases include chronic sinus infections dizziness headaches and facial pain.
Mucous retention cysts can appear in the maxillary sinus area from repeated sinus infections.
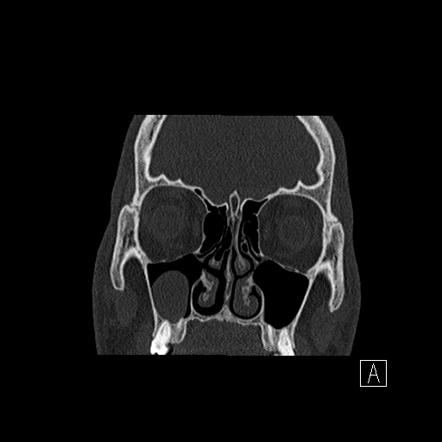
Retention cysts are seen on imaging as rounded dome shaped lesions often situated on the maxillary sinus floor.
Size and location are always different as well as the symptoms.
Cysts are closed pocket like formations of tissue and are filled with liquid air or semi solid material.
The collection of extravasated fluid develops a fibrous wall around itself forming a pseudocyst.
According to statistics every 10 th person has this disease.
Often their formation is due to chronic diseases.
The mucous retention cyst in the maxillary sinus is generally painless.
These cavities are called sinuses and they are located in the maxilla or upper jaw.
A blockage in the mucous duct can cause the gland to enlarge which can lead to the formation of a dome shaped maxillary mucous retention cyst.
A mucocele or mucous retention cyst is a benign pathologic lesion.
The cyst does not usually cause any symptoms and does not damage expand or thin the wall of the sinus.
A few cases may see facial pain headaches and sinus infections.
These cysts usually appear as rounded dome shaped soft tissue masses most often on the floor of the maxillary sinus.
They are slow growing lesions but mucosal and cortical integrity is preserved.
A mucous retention cyst in the maxillary sinus area usually does not show any symptoms.
They are usually found when an x ray or scan is done of the sinuses.